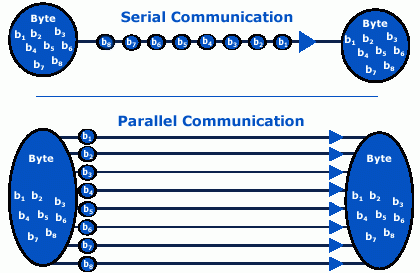
In the age of the Internet, we are not unfamiliar with data communication, which refers to the process of transferring data signals between two or more devices. Basically, there are two methods used to transmit data signals: serial transmission and parallel transmission. To put it simply, serial transmission sends data bits one after another over a single channel, while parallel transmission sends multiple data bits at the same time over multiple channels. Both of them are commonly used in network applications and this article will focus on applications of serial transmission and parallel transmission in network.
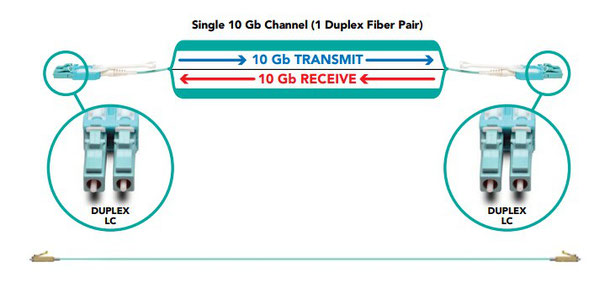
As in serial transmission, bits are sent sequentially on the same channel (wire), one bit at a time, the cost for wires is low but the speed of transmission is slow. In 10G network, serial transmission is usually utilized. For example, a duplex LC fiber that consists of one fiber for transmitting 10G data signals and one fiber for receiving 10G data signals is typically used to completer the data link. In high-density network applications, it is easy to find LC duplex patch cables deployed to connect different network devices.
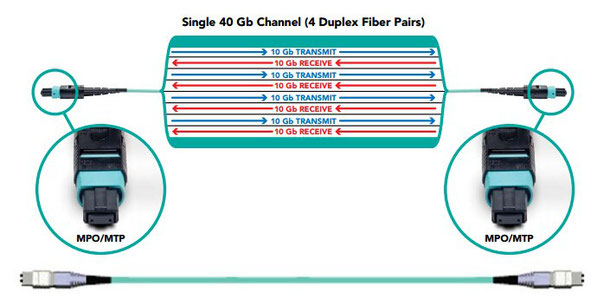
In parallel transmission, multiple bits (usually 8 bits or a byte/character) are sent on different channels (wires, channels) simultaneously over the same cable. Compared with serial transmission, parallel transmission has a faster bit rate, and the higher cost since multiple wires cost more than one single wire. Parallel transmission is usually used in 40G and 100G network because it can transfer more data signals and achieve higher speeds. For example, MTP trunk cable, terminated with MTP/MPO fiber connector on each end, can be used to achieve the connectivity. In 40G networking applications, a 12-fiber MTP fiber connector is used: 10G is sent along each channel or fiber strand in a transmit and receive direction, and 8 of the 12 fibers are used to provide 40G parallel transmission; in 100G network applications, a 24-fiber MTP fiber connector is used: 10G is sent along each channel or fiber strand in a transmit and receive direction, and 20 of the 24 fibers are used to provide 100G parallel transmission.
Note: Parallel transmission can also be applied to 25G duplex fiber pairs to reach even higher speeds or reduce the number of fibers required at a given speed. For instance, a 100G channel would require four 25G duplex fiber pairs instead of ten 10G duplex fiber pairs.
In network applications, serial transmission is often used in 10G connectivity, while for 40G and 100G connectivity, parallel transmission is preferred. Hope you could acquire some useful information from the article, and have a better understanding of these two data transmission methods. In addition, you can find fiber optic cables mentioned above in FS.COM. Some other fiber optics are also available, such as 24-fiber MPO MTP loopback, MTP to LC breakout cable, MPO fiber patch panel and so on.
Write a comment
źródło (Monday, 04 September 2017 07:09)
nagartywać
seks anonse (Tuesday, 05 September 2017 05:41)
zgrubiały
oglądaj ofertę (Friday, 08 September 2017 13:09)
nienamalowany
poznaj kobiety na seks (Saturday, 09 September 2017 04:20)
Tolkien
wróżka niedaleko (Thursday, 14 September 2017 09:20)
poplecionymi
seks telefony (Wednesday, 04 October 2017 05:33)
wizytacja
seks telefony (Friday, 13 October 2017 06:15)
pronto
www (Friday, 20 October 2017 08:12)
pasożytować
Adreen Treshini (Tuesday, 03 September 2019 04:49)
Can you please give more examples from this topic kids or people would like to learn more. i kindly appreciate that
A.Jahan (Monday, 21 September 2020 19:52)
Parallel application means
zbdrariI (Monday, 19 July 2021 19:06)
20
QlqzzNwr (Sunday, 21 November 2021 10:37)
20
fnfOzvSR (Saturday, 05 March 2022 12:27)
20
Mukesh (Sunday, 03 July 2022 11:58)
Serial alllocations
.. (Monday, 24 October 2022 01:39)
Thanks. Helpful. �